The Habsburg jaw, an exceptional facial function historically associated with the Habsburg royal circle of relatives, remains a topic of fascination and examination in both scientific and ancient contexts. Known for its reported prognathism (sticking out the decrease jaw), this genetic trait has become a symbol of the outcomes of inbreeding inside royal families. Today, the Habsburg jaw continues to appear in people, raising questions about its genetic inheritance, prevalence, and implications for current people. This article delves into the ancient background of the Habsburg jaw, its genetic origins, its presence in cutting-edge populations, and the scientific and social implications for people who possess this trait.
Historical Background of the Habsburg Jaw
The Habsburg Dynasty: A Brief Overview
The Habsburg dynasty became one of the most influential royal homes in Europe, with a reign that spanned numerous centuries. Originating in Switzerland, the Habsburgs rose to prominence within the late medieval period, ultimately controlling considerable territories including Austria, Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, and plenty of Central Europe. The dynasty’s electricity peaked at some stage in the Renaissance and Baroque periods, but their legacy endures, in part because of the distinct bodily developments of a number of its members. LadyBark
The Emergence of the Habsburg Jaw
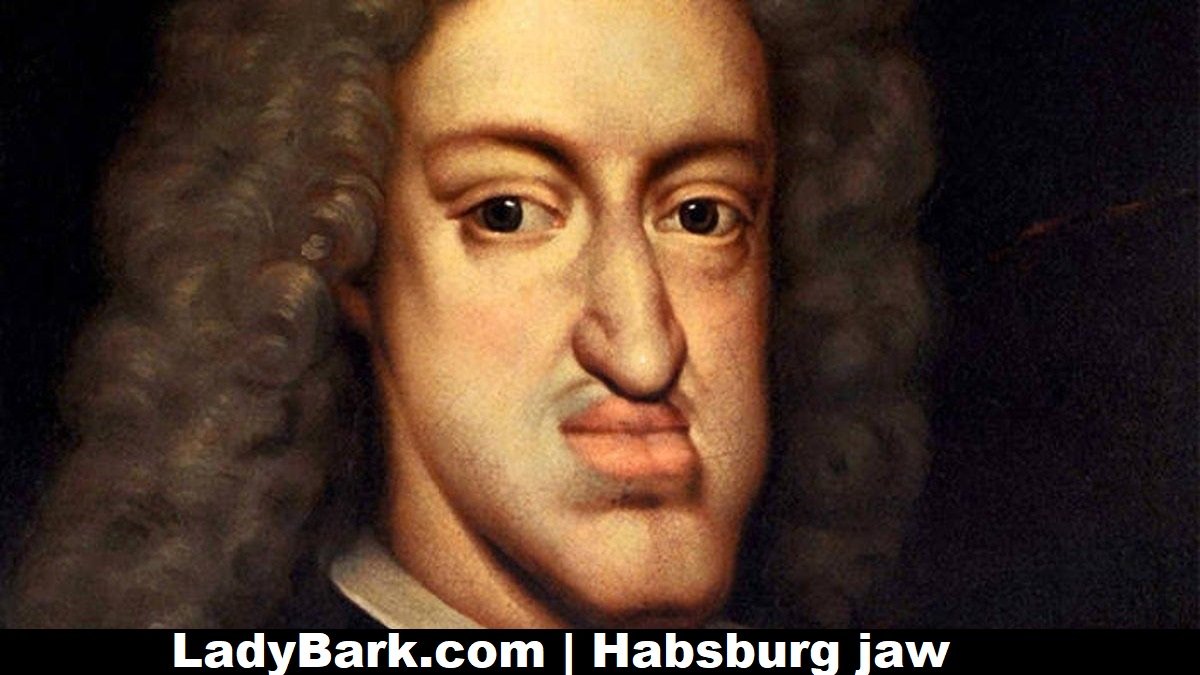
The Habsburg jaw became mainly first-rate in the fifteenth and 16th centuries, as intermarriage in the circle of relatives aimed to consolidate energy and preserve wealth. Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor (1459–1519), is often referred to as one of the earliest amazing figures to exhibit a pronounced jaw. Over generations, this trait has become more pronounced, culminating in figures like Charles II of Spain (1661–1700), whose extreme prognathism and related fitness problems exemplified the detrimental results of inbreeding.
Iconic Figures with the Habsburg Jaw
Several key ancient figures are often referenced while discussing the Habsburg jaw:
Charles V (1500–1558): Holy Roman Emperor and King of Spain, he exhibited a reported jawline and chin, making him one of the most recognizable carriers of the trait.
Philip IV of Spain (1605–1665): Known for his elongated face and jaw, his snapshots spotlight the characteristic functions.
Charles II of Spain: Perhaps the most intense instance, his severe jaw deformity was observed with the aid of numerous health issues, leading to his childless demise and the stop of the Spanish Habsburg line.
Genetic Origins of the Habsburg Jaw
Understanding Prognathism
Prognathism refers back to the positional dating of the mandible or maxilla to the skeletal base, wherein both jaws protrude beyond a predetermined imaginary line within the coronal aircraft of the cranium. In the context of the Habsburg jaw, mandibular prognathism (lower jaw protrusion) is the number one awareness.
Genetic Factors
The Habsburg jaw is taken into consideration as a result of genetic inheritance, with the robust concept of autosomal dominant trends playing a role. This way, the trait can be passed down from just one parent wearing the gene. Inbreeding, not unusual among European royalty to preserve electricity and wealth, likely exacerbated the superiority and severity of this circumstance within the Habsburg family.
Modern genetic research
Contemporary genetic research has attempted to pinpoint the exact genetic mutations responsible for prognathism. Studies have diagnosed several genes probably involved in jaw development, along with the MSX1 and PAX9 genes. However, appropriate genetic pathways and the extent to which they contribute to situations like the Habsburg jaw remain subjects of ongoing research.
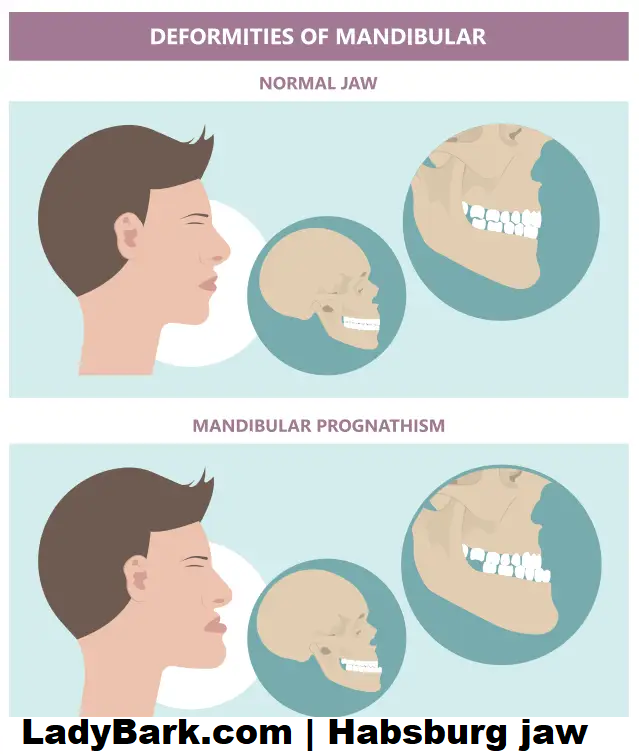
The Habsburg Jaw in Contemporary Populations
Prevalence
While the Habsburg jaw is traditionally related to a particular royal lineage, prognathism can and does appear in the widespread populace today. The condition is pretty uncommon, with various tiers of severity. It isn’t always restricted to any specific ethnic or geographical institution, though familial clustering indicates a genetic issue.
Modern Cases
Modern times of the Habsburg jaw may be visible in folks who might also or might not be privy to their genetic background. These instances frequently draw media interest, especially when connected to brilliant households or public figures. However, many cases go disregarded or are genuinely considered a variant of an ordinary facial shape. Also Read This Article Baby Blobfish
Diagnosis and identification
Prognathism is commonly identified through clinical exams and imaging research, including X-rays or CT scans. Orthodontists and maxillofacial surgeons often stumble upon this condition at some point in their checks for dental and skeletal irregularities. Genetic counseling may be advocated for households with records of the mentioned prognosis to recognize the inheritance styles and ability implications for future generations.
Medical and social implications
Health Concerns
Individuals with pronounced prognathism may additionally experience a number of fitness problems, consisting of:
Dental Problems: Malocclusion (misalignment of enamel), trouble chewing, and accelerated wear on a certain tooth.
Speech Difficulties: The structure of the jaw can affect articulation and speech patterns.
Respiratory Issues: In intense instances, jaw structure can contribute to obstructive sleep apnea and other respiration troubles.
Psychological Impact
The special appearance associated with the Habsburg jaw could have psychological and social implications. Individuals may additionally enjoy self-recognition or social stigma due to their looks. In some instances, this may cause issues with shallowness and social interactions, highlighting the significance of supportive environments and mental counseling.
Treatment Options
Several treatment alternatives are to be had for individuals with prognathism:
Orthodontic Treatment: Braces or different dental appliances can help with accurate enamel alignment and improve bite features.
Orthognathic Surgery: In more severe instances, surgery to realign the jaws can be advocated. This method, called orthognathic surgery, can notably improve characteristics and look; however, it involves a lengthy recovery period.
Speech Therapy: For those experiencing speech difficulties, speech remedies can provide techniques to enhance articulation.
Advances in Treatment
Advances in scientific technology and techniques have advanced the outcomes for people with prognathism. Minimally invasive surgical techniques, 3-D imaging, and customized orthodontic remedies have enhanced the precision and effectiveness of interventions. These improvements provide a wish for a better quality of life for those suffering from this situation.
The Habsburg Jaw in Cultural and Academic Contexts
Historical Significance
The Habsburg jaw serves as a poignant instance of the impact of genetic inheritance and inbreeding on human health. It has been the challenge of several ancient and clinical studies to present insights into the lives and demanding situations faced by ancient figures. The situation also underscores the importance of understanding genetic variety and the outcomes of close-kin marriages.
Representation in Media and Art
The one-of-a-kind appearance of the Habsburg jaw has been immortalized in numerous pictures and artistic endeavors, especially at some stage in the Renaissance and Baroque periods. These representations offer a visible report of the condition and its prominence among European royalty. Modern media keeps referencing the Habsburg jaw, often in discussions about genetics and ancient figures.
Academic Research
The Habsburg jaw remains a topic of interest in educational circles, especially in the fields of genetics, history, and medical anthropology. Research into the genetic foundation of prognathism contributes to our knowledge of human evolution and genetic issues. Historical analyses provide context for the social and political implications of the Habsburg dynasty’s genetic legacy.
The Future of Research and Awareness
Genetic counseling and education
As our understanding of genetics continues to develop, the function of genetic counseling will become increasingly vital. Families with a record of prognathism can benefit from counseling to understand the dangers and implications of the condition. Education about genetic inheritance and the importance of genetic variety can help mitigate the dangers associated with inbreeding.
Public awareness campaigns
Raising public consciousness about conditions, just like the Habsburg jaw, can reduce stigma and sell information. Educational campaigns can spotlight the significance of genetic research and the role of genetics in human health. By fostering a more knowledgeable public, we can create a more supportive environment for individuals with specific genetic tendencies.
Continued Research
Ongoing studies into the genetic foundation of prognathism and related situations are crucial. Advances in genetic sequencing and molecular biology keep promising for figuring out specific mutations and pathways concerned with jaw improvement. Collaborative research efforts across disciplines can result in new insights and capabilities for treatments for those suffering from those conditions.
Conclusion: Embracing Genetic Diversity
The Habsburg jaw, while a one-of-a-kind and often stigmatized trait, offers treasured instructions about genetic inheritance, historical contexts, and the importance of diversity. By knowing the genetic and social implications of prognathism, we will foster an inclusive and supportive society. Embracing genetic diversity and persevering with research into situations just like the Habsburg jaw will help enhance the lives of those affected and make a contribution to our broader expertise in human health and genetics.

